Sea Salt vs. Iodized Salt? Plastic & Lead-Free Brands.
Brown, Black, Pink…Which Salt is The Healthiest?
Sea salt vs. iodized Salt? Brown Salt, Black Salt, Pink Salt…
Q: mo, What do you think about Salt? Is it better to eliminate it, or is one Salt better than another? What about lead in Salt? Plus, what Salt do you use? Thanks– F.M.
A: F.M. Thanks for your salt questions. Let’s see what we can fit into today’s post.

Addressing first the question- Should I ‘just eliminate all salt?‘
Because our body needs Sodium, we shouldn’t aim to eliminate Salt altogether; instead, it’d be best to consume the best Salt we can afford, up to the recommended 1/4 teaspoon a day total.
Our Body Needs Salt:
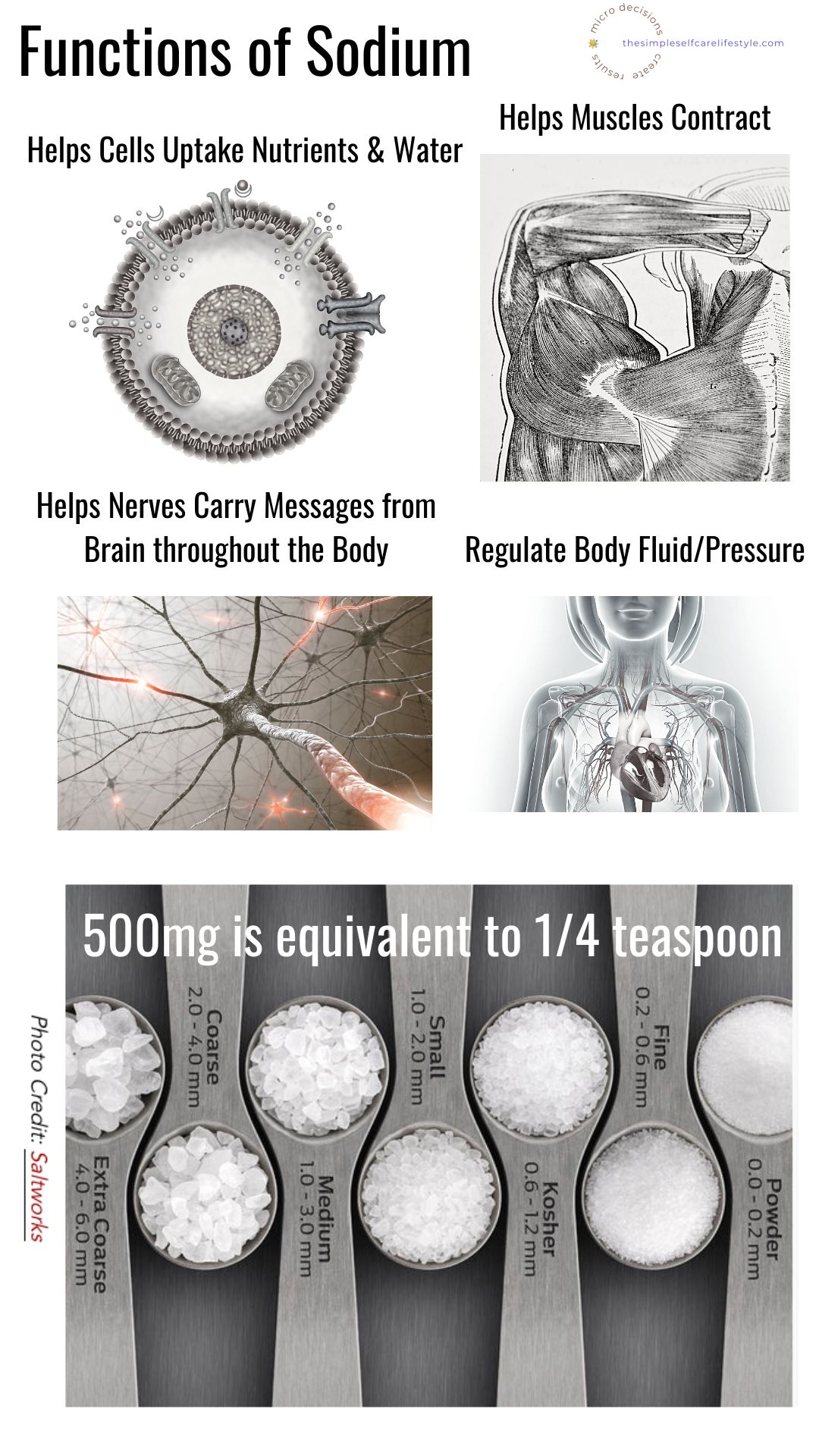
Our body needs sodium right down to our cells. We covered in Core Concept 1 of our 1 FOCUS that it is our CELLS that we depend on for our existence. It is essential to Provide our CELLS with optimal salt quantities consistently.
The human body requires a small amount of sodium to conduct nerve impulses, contract and relax muscles, and maintain the proper balance of water and minerals. It is estimated that we need about 500 mg* (a bit less than 1/4 teaspoon) of sodium daily for these vital functions.
(1)(bold and * added) *.
According to the Mayo Clinic:
1 teaspoon of table salt, which is a combination of sodium and chloride, has 2,325 milligrams (mg) of sodium.
(3)(bold added)
It works out that we ‘need’ less than a 1/4 teaspoon to meet the recommended daily requirement.
Most of us easily exceed that and are asked to stay under 2,300mg daily, which is approximately approx. One teaspoon per day.
The typical recommendation for those trying to reduce blood pressure is to stay under 1500mg daily.
Harvard provides this chart of a variety of popular salts. Sodium amount per teaspoon. (1)
Sodium is the most abundant electrolyte ion found in the body.
(4)Salt and sodium. The Nutrition Source. Harvard School of Public Health
Both Sodium and Chloride (which make up the majority of all salt) are electrolytes our body needs.
An electrolyte is a chemical that conducts electricity.
The ‘electrical’ charge is how the electrolytes conduct the electrical currents needed for our:
- Nerves
- muscle contractions.
- ability to rebuild damaged tissue
They also balance our:
- hydration
- blood acidity
- and blood pressure…
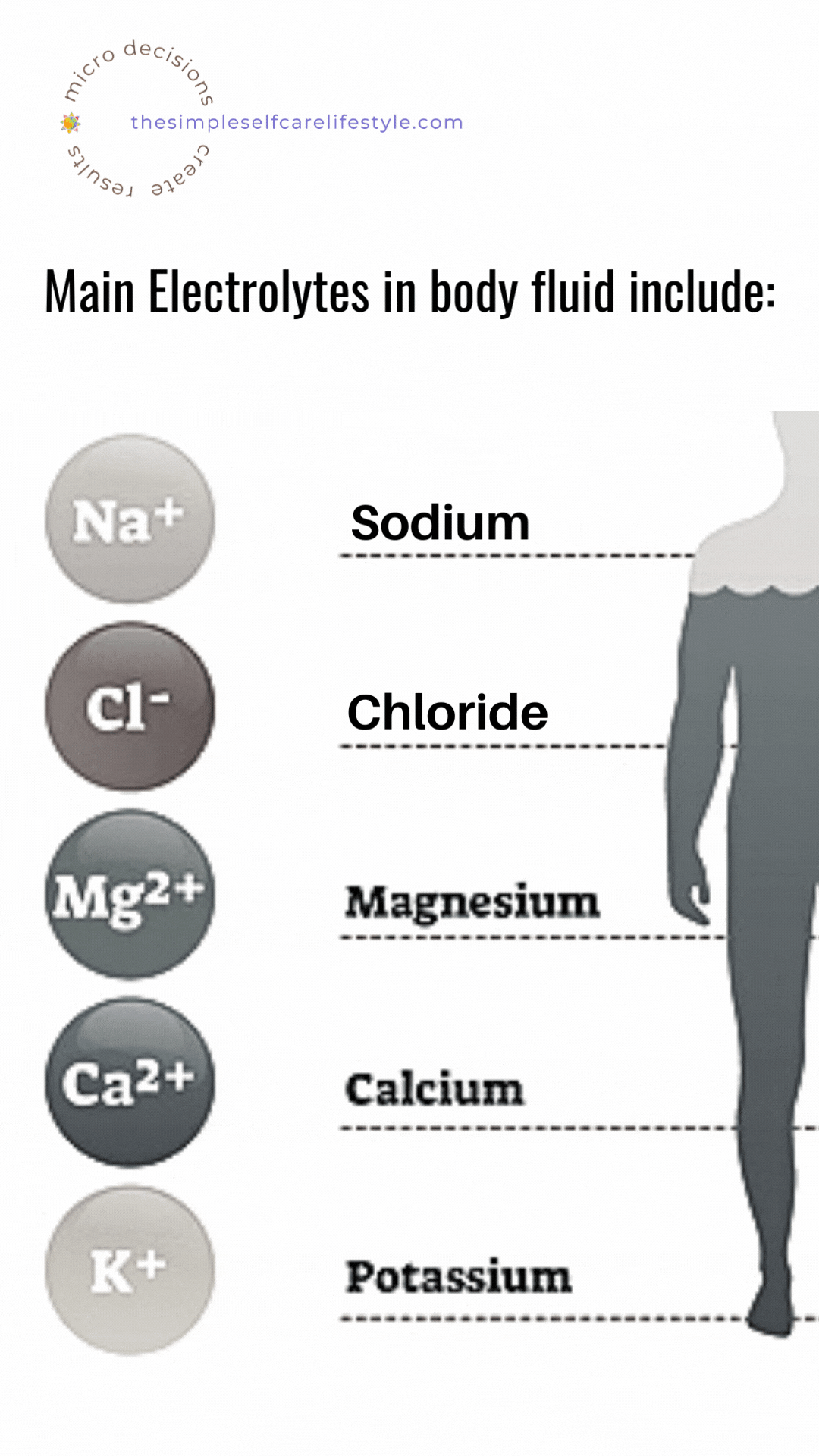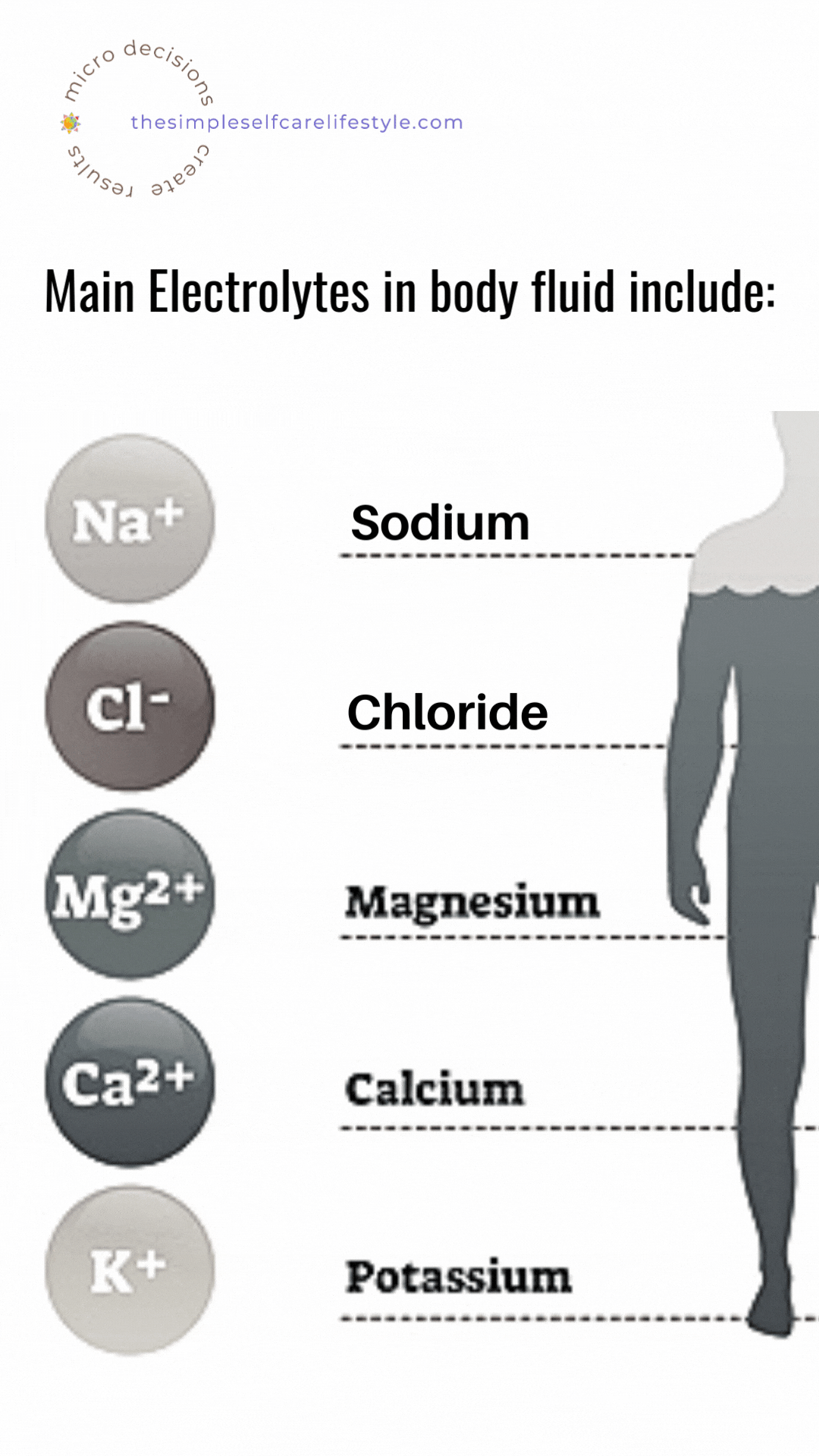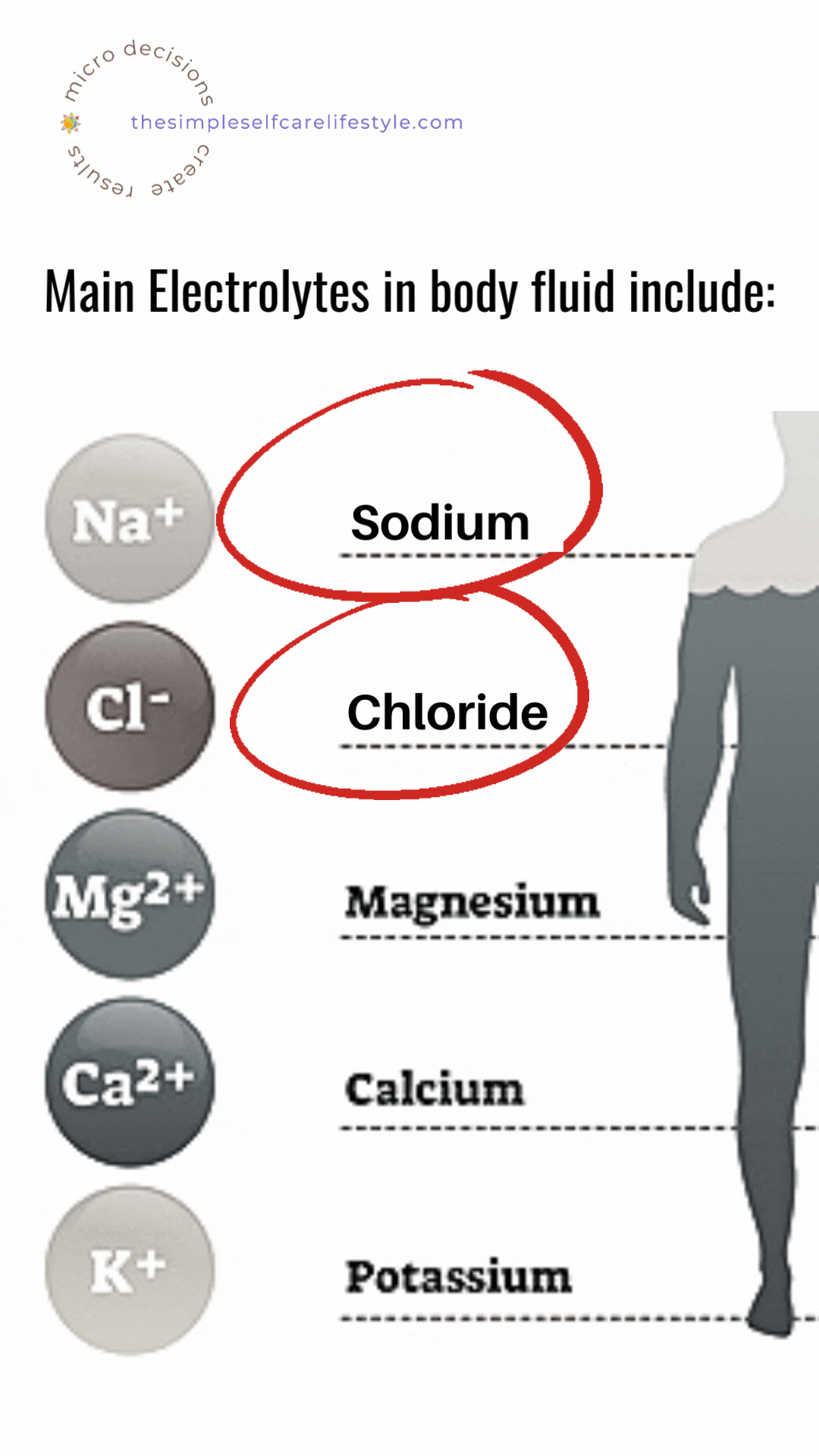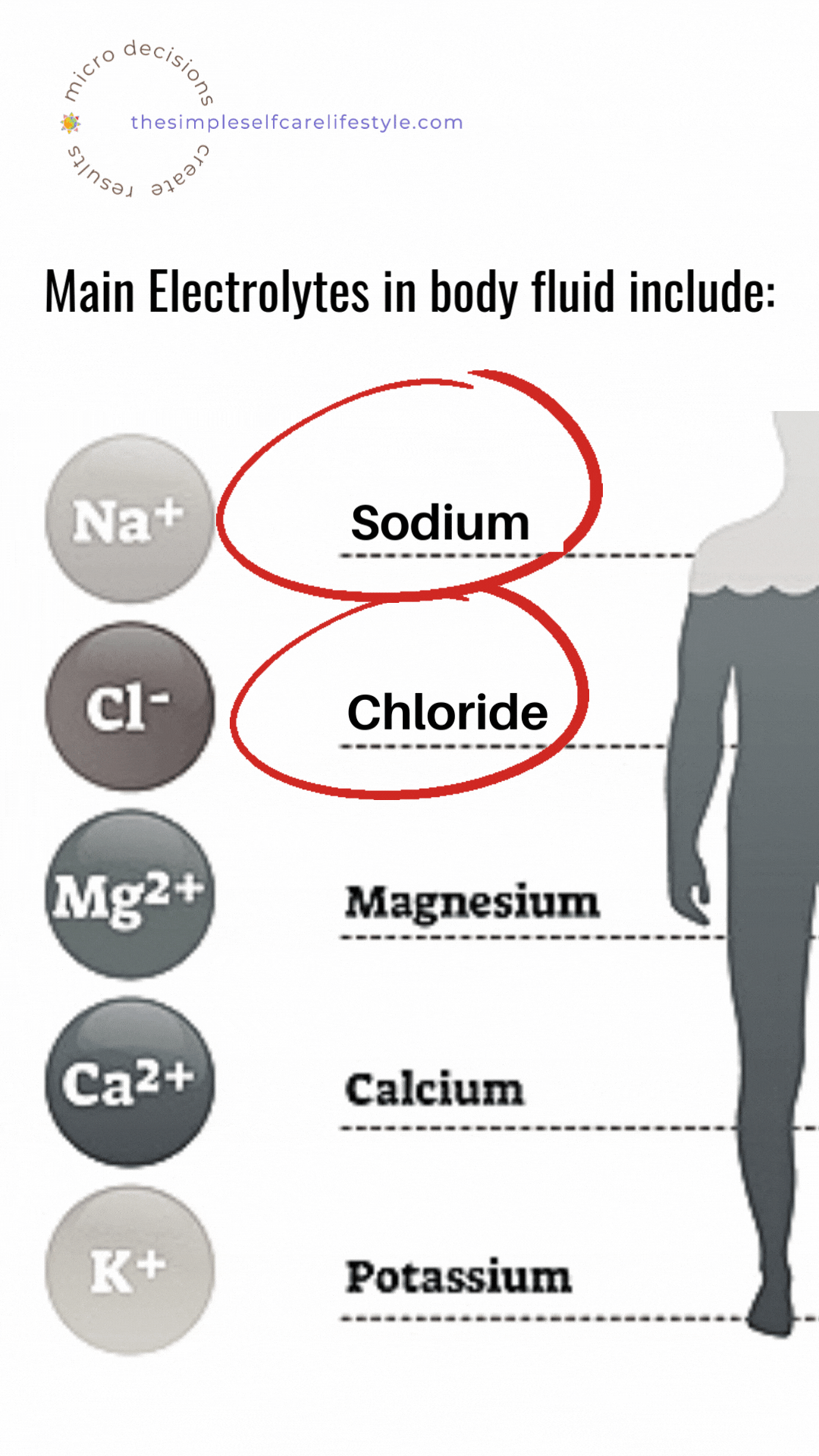
There are six very important electrolytes:
- sodium,
- potassium,
- chloride,
- bicarbonate,
- calcium, and
- phosphate. (5)
Salt provides 2 of them.
If Salt is Too Low
If salt is too low- especially if it is chronically too low, it can negatively impact many bodily functions and create: (15)
- Confusion
- Loss of energy
- Drowsiness and fatigue
- Restlessness and irritability
- Muscle weakness, spasms, or cramps
- Seizures
- Coma
Low Salt Disrupts Sleep:
Researchers found that very low-salt diets may contribute to sleeping issues. (11)
Salt Supports Digestion:
Salt activates an enzyme in the mouth called salivary amylase. Amylase is an important enzyme that helps us break down carbohydrates into smaller molecules.

Salting Meat Before Cooking Can Help Its Digestion
Protein that has been salted prior to cooking can help make it easier to digest.

Cooking With Salt Can Help Maintain and Bring Out More Nutrition in Whole Foods.
Dissolving (a small amount) of salt in the water before cooking your vegetables can help it retain its nutrients. (20) OFTEN, you can eliminate the need to salt your food after.
Using salt – before you cook or when you cook, can add:
- Flavor
- Nutrition
- Vibrance and
- Texture
to your cooked foods.

While Sodium benefits are often well known, Chloride in salt also offers a multitude of benefits.
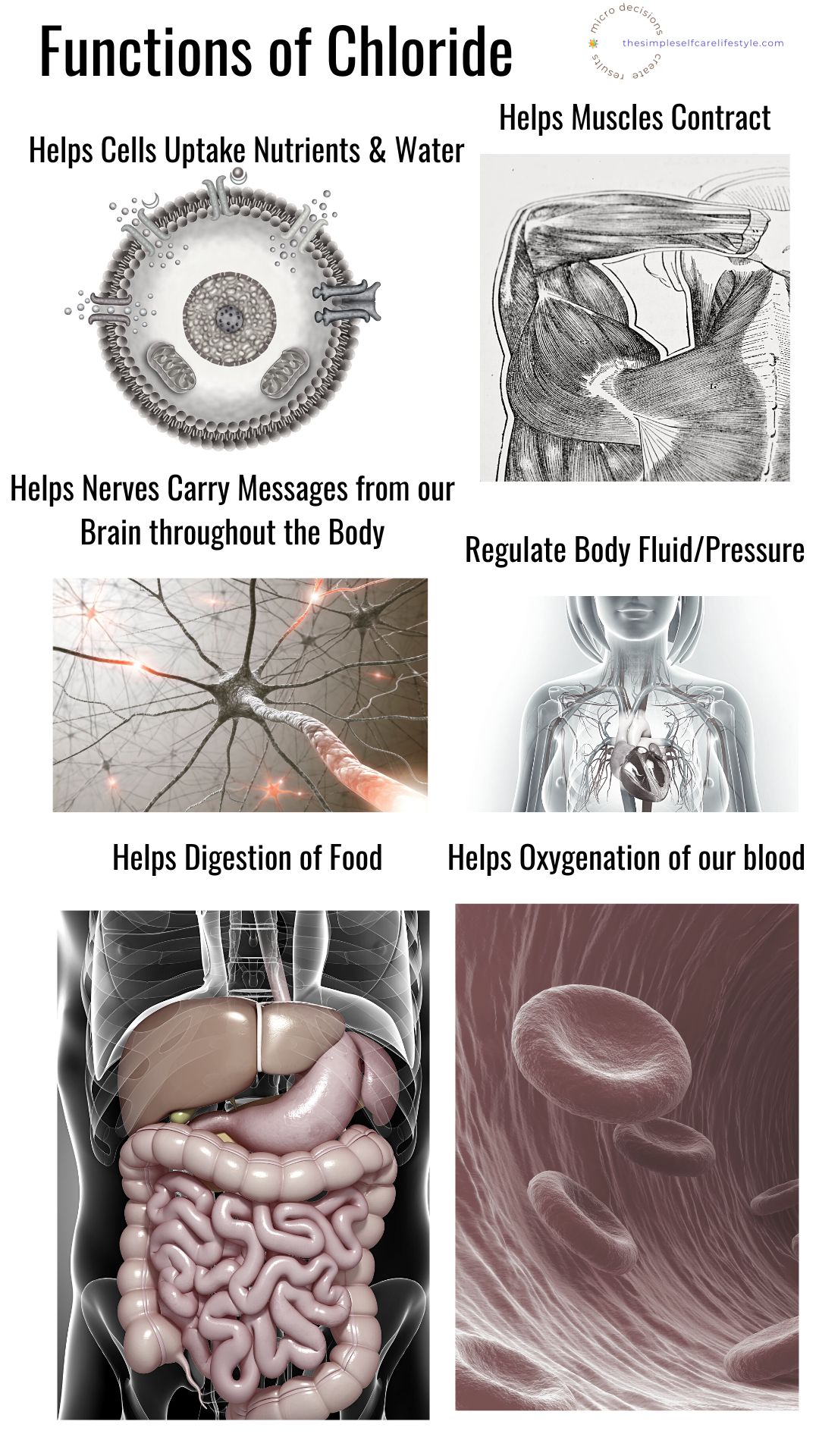
Salt Can Support Stomach Acid
Yet another very important function of salt- when consumed in balanced amounts, it supports our stomach acid.
The right amount of sodium and chloride improves digestion. (9)
Post: Indigestion
#1 Cause of Indigestion…
Feel Better, Look Better, & Live Better than you ever imagined!
Self-Care information, tips, tools, products & programs
Bottomline: Our Body Makes Good Use of Salt
Like sugar, too ‘little’ Salt in our diet is not typically an issue.
On the contrary, the majority of people exceed the recommended daily amount by a lot.
Re-Cap:
Our body makes good use of salt.
We need some salt, and too little or total avoidance could mean we may not have enough sodium and chloride electrolytes, which can negatively impact multiple body systems.
I believe working with your practitioner to find the amount that works for your body is best.

Balancing the amount of Salt YOUR body needs is the key:
There’s a breaking point where above a point you start seeing harm, and below a point, you also start seeing harm,”
(6)
says Dr. Andreas Kalogeropoulos, an assistant professor of medicine in Emory University School of Medicine’s Division of Cardiology,...

Sea Salts vs. Table Salts: Is One Better?

Sea Salt is better but not because of major nutritional differences.
In general, all salts, sea salts or table salts, are mostly sodium and chloride. (2)
Sea Salt can be the better choice IF you have the option to choose a brand that has open access to its:
- sourcing information,
- processing methods, and
- independent testing results.

The health impact differences between Table/Sea Salts stem from:
- where they are sourced
- the processing methods
- what is deleted/added
which impacts the
- mineral content in the salt
- lead/metals found in the salt
- microplastics found in the salt

Post: Microplastics in our Tea bags
Even Organic? Yup! Billions of Micro and Nanoparticles per cup.
Feel Better, Look Better, & Live Better than you ever imagined!
Previous Post: Microplastics in your teabag
Where Salts are Sourced Matters
Let’s start with where salts are sourced ‘in general’ and then focus on the ‘best’ of those sources I have found.
Brands that have the minerals/trace minerals we’d like in our salt without the additives of table salt, lead, and microplastics that can be found in both table and sea salts.
This way, we can attain the
- sodium
- chloride and
- trace minerals
while protecting ourselves and our families from the:
- additives
- lead and
- microplastics.

Where Salts Come From (In General) by Type
Sea Salts and Table Salt both come from natural sources.
Sea salts are sourced from saltwater lakes/bays/ocean water.
Table Salt (Iodized salt) is typically mined from underground deposits.
‘Typical’ Manufacturing Process for Each.
Sea salts come from the evaporation of seawater/saltwater lake/bay and have minimal to no processing.
Table Salts come from brines created from extracted mined salt.
They are striped of ‘other’ minerals and then have anti-caking agents and iodine added.
Anti-caking additives that may be used in salt include but are not limited to: (13)
- Calcium silicate
- Sodium ferrocyanide
- Potassium ferrocyanide
- Calcium ferrocyanide
- Talc
- Aluminum silicate
- Iron Ammonium Citrate
- Yellow prussiate of soda
Iodine is added to table salt to help prevent iodine deficiency. This industry standard has been around since the 1980s in an effort to Salt universal salt iodization. (14)
That’s a whole different topic.

Natural Non-Toxic Cleaner That WORKS!
EPA-registered sanitizer kills 99.9% of viruses- Flu & COVID, bacteria, and mold… SAFE for you, your children, and your pets!
Photo Credit: List source of image

Sea Water to Salt Process Example Specific to Saltwerk Sea Salt
Here is a direct description of how Saltwerk processes its salts from the sea:
“We pump the seawater to open pans where we pre-heat it until it becomes a strong brine, a salinity level of 17-20%.
Then we boil the brine until white crystals appear on the surface and slowly fall to the bottom of the pan.
We draw the pan and drain any remaining liquid.
It is dried and put into packaging.”

Bay Water to Sea Salt Process Example
Specific to Jacobsen Bay Water Sea Salt
Here is a direct description of how Jacobsen processes their salts from bays:
“Seawater is pumped from Netarts Bay, filtered, and then transferred into our reverse osmosis machine, where it’s further filtered and reduced to concentrated salt water, which is called prebrine.
Prebrine is pumped into large boil tanks where excess minerals are removed, and the prebrine continues to reduce down to brine.
Brine is then pumped into custom-made evaporation pans and carefully heated, creating beautiful sea salt…
The salt is gently scooped from the pans, rinsed, and put onto racks in a dehydrator for drying…
Once dry, every flake of salt is graded, sifted, and sorted.“

Underground Mining Table Salt Process Example
Iodized Table Salt is typically mined from underground deposits and processed to remove other minerals,(1) it is enriched with iodine*, and anti-caking agents are added.
*The process of iodizing involves adding a small amount of potassium iodide to the salt crystals they form.
A Direct Description of the Table Salt Process
“hydraulic mining (or solution mining) of salt involves pumping water below the earth’s surface to dissolve salt deposits and create a salt brine.
This brine is then pumped to the surface and evaporated to create salt.
The salty brine may be treated prior to evaporation to reduce mineral content, yielding a nearly pure sodium chloride crystal.
This method is inexpensive, has a high yield, and produces a very clean salt”…. “depending on the type of salt it will be, iodine and anti-clumping agents are added to the salt. Most table salt is produced this way..”(3)(7)(8)(bold added)

Are There Nutritional Differences?
Yes. There are differences when it comes to minerals and trace minerals of the different salts.
But research indicates there is NOT a big difference.
Here is what current research provides us.
They All Have Sodium and Chloride. The Small Remainder Varies Greatly.

The content of all Salt is mostly sodium and chloride.
The charts at the beginning of the post-show that each type of salt fulfills our sodium need with less than a 1/4 teaspoon.*
In the past and now, when writing this post, I have scoured for actual research listing the nutritional differences between table salt and sea salts.
We know table salt has sodium, chloride, and no additional minerals or trace minerals, zero, nada because it has been stripped in the processing. That is the industry standard. (Iodine is added, plus anti-caking agent(s).
So we know the mineral content in Table Salt.
To compare sea salts, the BEST analysis I have found to date is in An Analysis of the Mineral Composition of Pink Salt Available in Australia. Foods. (Linked for you in the references and resources section)
In this research, they compare data that includes mineral /heavy metal composition as well as nutrient data of multiple pink Himalayan salt brands. You can take that data and then compare it to Table Salt data and individual salt producers.
The best conclusion I have been able to deduce over the years is that Sea Salts definitely have more minerals and trace minerals, but the amount is small (better than none but small).
The amount of minerals and trace minerals is dependent on the region, processing…
The amount of minerals and trace minerals is dependent on the region, processing…
So the NUTRITIONAL differences are not what I am basing my decision on when it comes to deciding whether I consume Sea Salt or Table Salt.
I CHOOSE SEA SALT AS THE ‘HEALTHIER’ CHOICE (with a caveat)
It is true we can say Sea Salts are a bit healthier with their minerals and trace minerals, but it isn’t a ‘big’ nutritional difference that can definitively make sea salt the healthier choice.
Instead, it is what ISN’T in Sea Salt that makes it a ‘healthier’ choice for our bodies.
Anti-Caking Agents
Anti-caking chemicals are not added to Sea Salts as an industry standard.
And since our cells are not in need of anti-caking chemicals for them to thrive, on the contrary -it adds one more ‘thing’ for our body to ‘take care of’ and eliminate; therefore, I choose Sea Salt
Heavy Metals Like Lead & Micro Plastics
Next, there is the question of how much lead/heavy metals and Micro Plastics are in your salt.
Again, our CELLS, which we are dependent on, DO NOT NEED LEAD and or MICROPLASTICS.
F.M., you also asked about lead (I’m adding microplastics to the mix).
Both Table Salt and Sea salt are routinely tested to have lead/heavy metals and plastics in them.
This is why I say Sea Salt is the better choice, with a caveat.
(For more on protecting yourself from microplastics 🔗 Plastics in your tea bags. Billions per cup)

Sea Salt Is Better With The Caveat That It Is NOT Laden With MicroPlastics and or Lead/Heavy MeSalt
Whether You Choose Table Salt or Sea Salt, KNOW Your Brand.
Lead and Salt
Salt has lead in it. Table Salt and Sea Salt BOTH have lead in them.
Our bodies and brains do not need us to consume any amount of lead.
This is why when researching the salts for my family (and previous clients), I always asked for lead/metal values that were tested by a third party.
Lead is a HUGE topic.
See if you can reduce your exposure to both by swapping your salt with one of the brands below.
When I began updating the research and resources for this post, I came upon a blog by Tamara Rubin. She has done a ton of research on the topic of lead and has collaborated with many others for brands of salt.
I was pleased to see that the two salts I use on the top list of her list too.
She lists her salt choices by groups of ‘safe’. Group 1 Salts are the ones she considers BEST CHOICES and 100% acceptable.
If you want more details on the lead in salt, I have listed and linked Tamara’s post in the resources and references list for you.

Sea Salt/Himalayan Sea Salt
Sea salt does contain small amounts of naturally occurring minerals/trace minerals, but it’s been demonstrated–
… that sea salts harvested from different parts of the world have different mineral content”
(10)(11)
“ … that sea salts harvested from different parts of the world have different mineral content” (10)(11)
And that although these minerals and trace minerals can and do contribute to well-being, the wide variance in the amounts, combined with the tendency to have higher heavy metal content, it can be very difficult to fetter out the best salt for our health and the health of our family. (10)
The sea salts I use have the lowest levels on the market.
To dig deep into the salt content/metals…#10 on the Reference list is filled with data.
Microplastics
Table Salts have microplastics
Now, new research shows microplastics in 90 percent of the table salt brands sampled worldwide.
(16)(18)(24)(bold added)
“Now, new research shows microplastics in 90 percent of the table salt brands sampled worldwide.” (16)(18)(24)(bold added)
Sea Salts can have microplastics
“The most common microplastics identified in the edible salts were polyethylene, polyester, and polyvinyl chloride derived from marine and salt-processing units.” (25)(bold added)
We Have a Plastic Problem.
The most common microplastics identified in the edible salts were polyethylene, polyester, and polyvinyl chloride derived from marine and salt-processing units.
(25)(bold added)
Everywhere we turn these days, we learn more and more about how microplastics are being consumed by us.
The simplest way to protect ourselves and our families is to focus on the items we consume the most and then find the brands with the least amount of microplastics.
Salt is one of those items. For some, Tea is another.

Post: Microplastics in our Tea bags
Even Organic? Yup! Billions of Micro and Nanoparticles per cup.
Feel Better, Look Better, & Live Better than you ever imagined!
🔗Post microplastics in our tea bags. Billions of them!
Salt has microplastics. We use a lot of salt. Day in and day out.
Here is the answer to the BIG salt question we started with.
SOOOO Is one salt better than another?
Yes, Sea Salt that is plastic-free with the lowest in lead/heavy metals is the BEST Salt!
What Salt I Use:
Those of you who have known me for years/even decades know my goal is to always research, contact, and vet products that support the body and reduce/eliminate exposure to toxins for myself, my family, and now you, my subscribers 💌😌
RE-CAP & The Salts I Use
RE-CAP
- Our body has a need for salt
- 1/4 teaspoon is typically enough to fill that need * unless there’s a bio-individual need for less or more.
- Balancing the amount YOUR body needs is the key.
- Table Salt and Sea Salts are from natural sources
- Sea Salt comes from Sea/Bay/Salt lakes
- Table Salt is mechanically mined from underground deposits, stripped of minerals, and has iodine and anti-caking agents added.
- Sea Salt is the better choice IF it is LOWER in Lead/Metals than your Table Salt and
- Your Sea Salt is without Microplastics.
Now the salts I use and recommend when asked.
I use Jacobsen Sea Salt and Saltwerk Sea Salt

The Specific Salts I Use From Each & Why
First, Jacobsen Salt Co
For Jacobsen, I specifically use ‘their’ salt. Harvested and processed directly from them. Not their imported partner salts.
Why?
The reason: it was their recommendation when I initially spoke with them. I wanted microplastic-free and lead not detected.
They now have the lead and plastics info on their Questions/facts page.
Direct quote from their facts page for you:
“Lead:
Our last analytical data for our Oregon Sea Salts, dated September 16th, 2022, from OMIC USA Inc. reported Lead was not detected to an LOQ of 20 ppb.
Our Fine Italian Sea Salt is from Trapani, Italy, and is harvested in a centuries-old tradition. As such, there are trace amounts of lead detected, 100 ppb in testing to a LOQ of 20 ppb. Our most recent laboratory analysis was performed by OMIC USA Inc. on February 5, 2021.
Our Pink Himalayan Salt is mined from ancient ocean beds and has a higher mineral content than any other salt we offer. Testing from our suppliers shows this salt to have a lead count average of fewer than 500 ppb. If you are concerned about lead levels, we suggest using our Sea Salt / Kosher Sea Salt as a substitute. (I added bold)
Microplastics:
Sadly, microplastics are present in our oceans. The filtered seawater we use is tested semi-annually by Polyhedron Laboratories. The last test was performed on June 1, 2021, and no microplastics were detected. All of our incoming seawater is filtered through a 0.5-micron filter (equivalent to 0.0005mm).
Potential Radioactive Isotopes:
In the wake of the devastating Fukushima nuclear disaster, we have had concerns about the lasting impact on our oceans.
We sent samples of our salt to the Center for Health Protection, Radiation Protection Services of the Oregon Health Authority. A low-level gamma spectrometry analysis reported no radioactive isotopes were present to a LOQ of 5 becquerels per kilogram.
The most recent testing for Salt radiation was performed in October 2020.”
They offer their salts through Amazon.
Next Saltwerk
Saltwerk
I use and gift a lot of Saltwerk. Last year I paid to have a bunch shipped over from Iceland for myself and gifts.
A month later, I found out they, too, are on Amazon.
‘Safe Lead’ Saltwerk Lead.
The ‘safe’ recommendation for lead is to be below 100 ppb for daily consumption. Saltwerk lead is below 30ppb
I personally choose to have salts 30 ppb and below.
Having access to Jacosen and Salterk makes it a possibility. 😁
There you go- The Salts I Use and Why.
Thanks for your email F.M.!
🧂Do you have an ultra-clean sea salt that you’d like to share or
❓ A different salt question?
I’d love to hear from you. You can reach me via email: 💌 [email protected]

A few related posts you may like and then References & Resources for today’s post below.

🌿 References/Resources for you
8. Freeman, S. (2022, August 12). How salt works. HowStuffWorks Science. Retrieved January 31, 2023,
additional references
References continued
16. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 21, 12819–12828 Publication Date:October 4, 2018 © 2018 American Chemical Society
19. Blog: How Jacobsen Salt Co.’s Water Filtration Prevents Microplastics
20. Book: NOSRAT, S. A. M. I. N. (2019). Salt, Fat, Acid, Heat. CROWN Books. Nosrat, S., MacNaughton, W., Pollan, M., & Blind, S. (2019). Salz, Fett, säure, Hitze: Die vier elemente guten kochens. Kunstmann.
References continued
21. Ujjaman Nur AA, Hossain MB, Banik P, Choudhury TR, Liba SI, Umamaheswari S, Albeshr MF, Senapathi V, Arai T, Yu J. Microplastic contamination in prSaltsed and unprocessed sea salts from a developing country and potential risk assessment. Chemosphere. 2022 Dec;308(Pt 2):136395. Salt 10.1016Salthemosphere.2022.136395. Epub 2022 Sep 9. PMISalt6096307.
22. Di Fiore C, Sammartino MP, Giannattasio C, Avino P, Visco G. Microplastic contamination in commercial salt: An issue for their sampling and quantification. Food Chem. 2023 Mar 15;404(Pt B):134682. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134682. Epub 2022 Oct 20. PMID: 36279784.
23. A Review of Microplastics in Table Salt, Drinking Water, and Air: Direct Human ExposureQun Zhang, Elvis Genbo Xu, Jiana Li, Qiqing Chen, Liping Ma, Eddy Y. Zeng, and Huahong ShiEnvironmental Science & Technology 2020 54 (7), 3740-3751 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b04535
24 Lee, H., Kunz, A., Shim, W.J. et al. Microplastic contamination of table salts from Taiwan, including a global review. Sci Rep 9, 10145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46417-z
25. Vidyasakar A, Krishnakumar S, Kumar KS, Neelavannan K, Anbalagan S, Kasilingam KSaltinivasalu S, Saravanan P, Kamaraj S, Magesh NS. Microplastic contamination in edible sea salt from the largest salt-producing states of India. Mar Pollut Bull. 2021 Oct;171:112728. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112728. Epub 2021 Jul 22. PMID: 34303058.
* unless you are sweating a lot, exercising a lot, sick,…
Products for Your Home
Non-toxic Kitchen, Laundry, Bedding, & Living Space Products…
Things I Always Keep Handy
Products For Life’s Little Emergencies: Bandaids, Charcoal, Clay, Arnica, Oreganol…
Quality Food Sources
Sources of High Quality: Ghee, Honey, Meats, Salts, Teas…
Supplements
Vitamins, Minerals, Cell Salts, BACH, Quality Sources.
Self Care Programs
The Simple Self Care Lifestyle Programs
The Simple Self Care Lifestyle
self care
Post categories