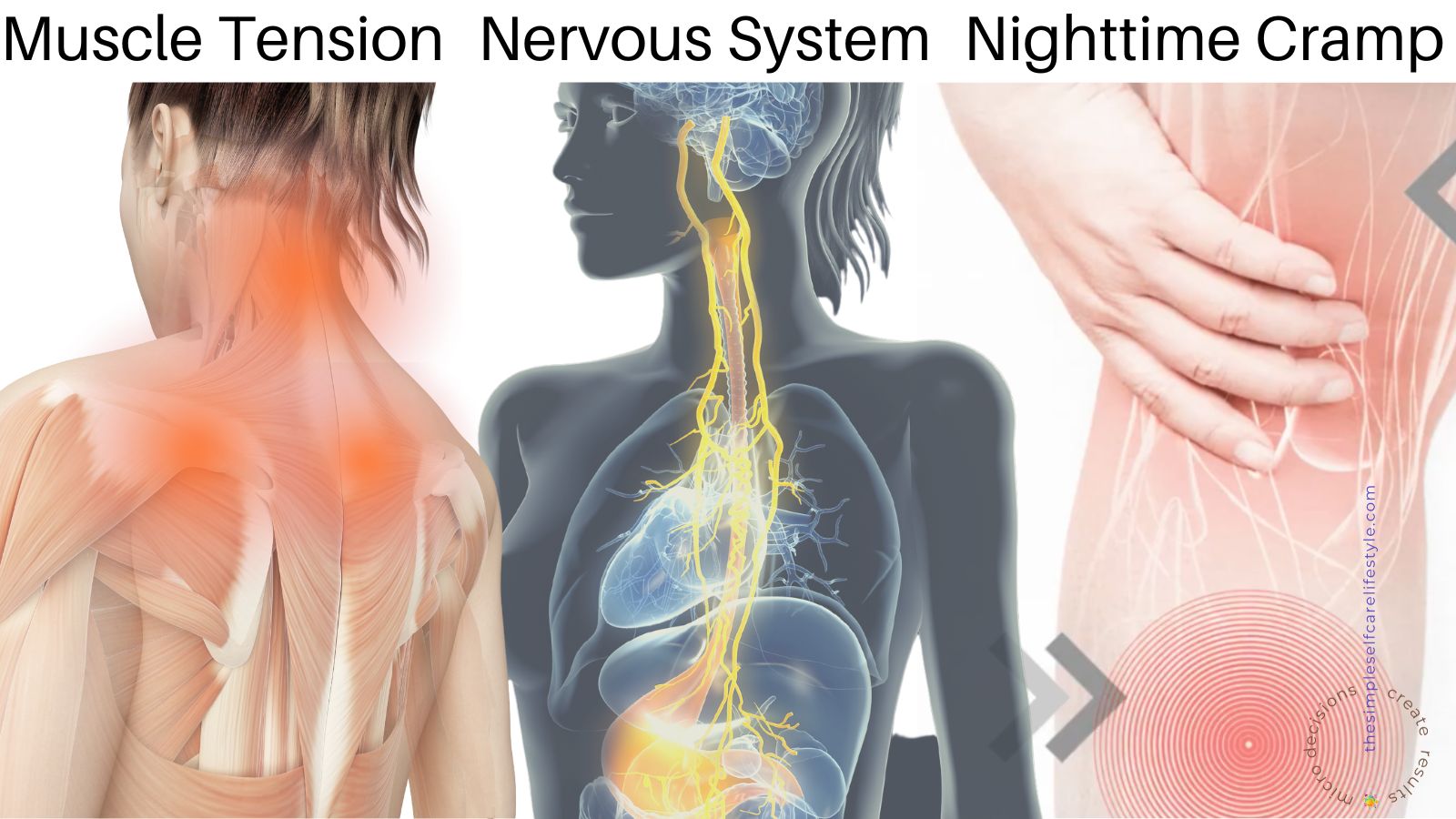
Relieving Leg Cramps
Relieving Leg Cramps is on the minds of many lately. I’ve received multiple emails specifically asking about relieving and preventing leg cramps at night, which makes perfect sense in light of the extraordinarily extreme weather most of us have been experiencing.
If you’re experiencing nighttime leg cramps, you are not alone!
Up to 60% of adults get leg cramps at night, as do up to 40% of children and teenagers.”
(1)

Some of the email questions:
“Hi, mo. Can you tell me what could be causing the terrible pain in my legs during the night? And what should I do during the cramp? “
“Greetings mo, A couple of questions: Why is the cramping in my leg at night so painful? And Is there a way to prevent them?“
“Why do we have painful foot and leg cramps while sleeping?”
“Dear mo, Are there Simple Self Care tips that help diminish nighttime cramps or even prevent them from happening?“
“What should I take for night leg cramps?”
…, researchers found that about 30% of adults report having NLCs (nocturnal leg cramps) at least five times a month.” “A high 6% reported nightly leg cramps”
(2)(bold added)(5)
Anyone who has experienced nighttime leg cramps knows they are painful, for some excruciatingly painful. I hope today’s information helps you match simple self care tips that work for your body.
Today we’ll identify:
- What a Nighttime Leg Cramp is.
- “Why is it so painful?” “What to do.”
- Why do our muscles cramp, to begin with?
- “What could be causing leg cramps?” (Common Causes)
- Simple Self Care Tips for Each of the Common Causes.
What is a Nighttime Leg Cramp?
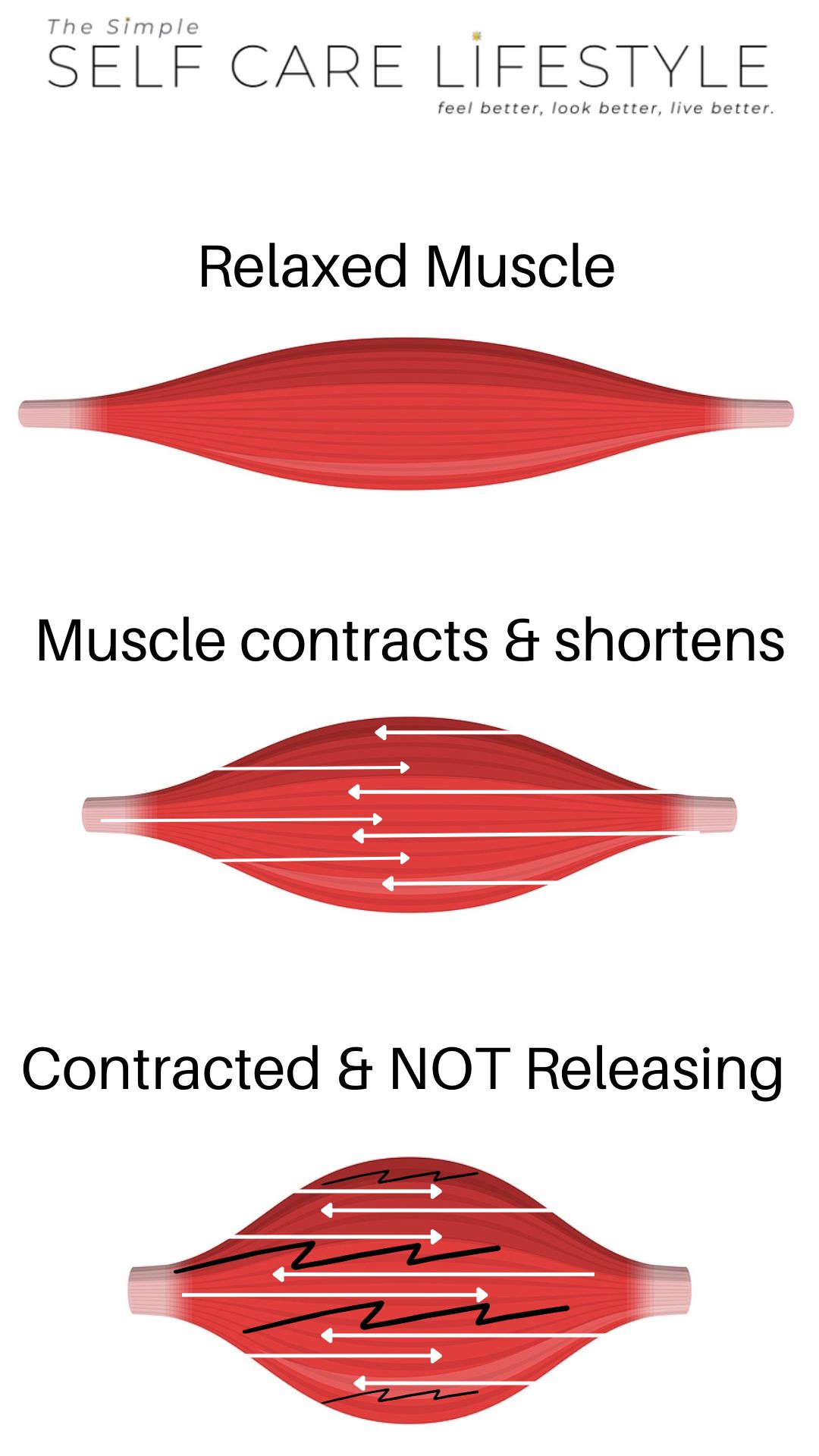
An NLC nocturnal (nighttime) leg cramp is the involuntary tightening of a leg muscle that, once contracted, does not have what it needs to relax again.
…NLC or nocturnal leg cramps are involuntary muscle spasms anywhere in the leg, though they are most common in the calf.
(2)
While asleep, the relaxed Leg or Foot Muscle involuntarily tightens and then basically gets stuck in the contracted state.
Why is a Nighttime Cramp so Painful?
Research identifies that the pain experienced during a muscle cramp begins with diminished blood flow to the muscle tissue, which sets off a cascade.
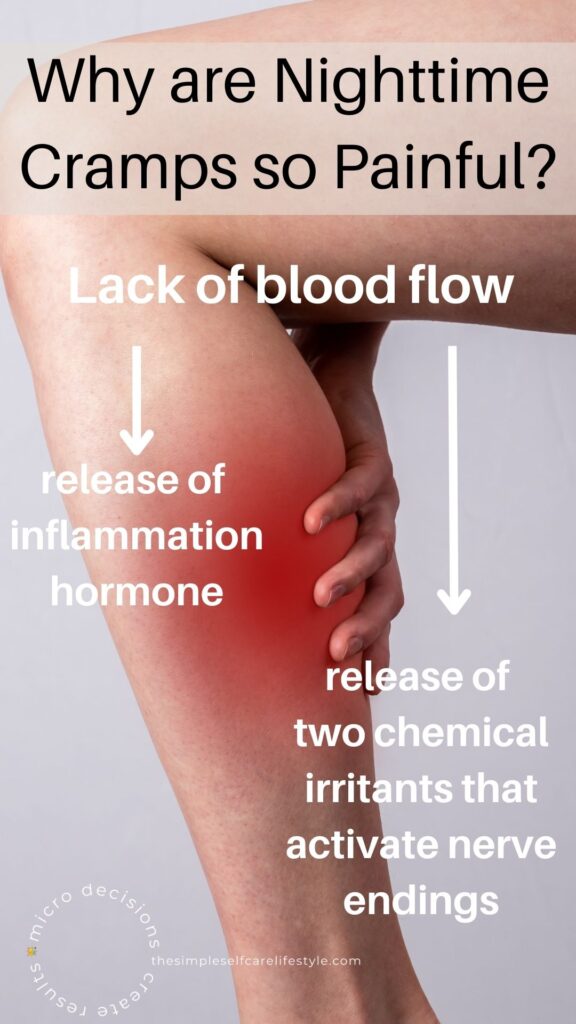
A muscle cramp is painful, sometimes excruciatingly painful, due to the cascade of events:
- a lack of blood flow leading to a change in pH (alkaline/acidity balance), this signals
- the release of a hormone (bradykinin) that produces inflammation (16), plus
- two chemical irritants: 1. a signaling molecule (ATP), and 2. protons (H+ ions), both of which activate nerve endings. (14)
Lack of Blood flow ➡ Lowers pH ➡ Sets off Inflammation ➕ Two nerve irritants 🟰 Pain
..
“The main reason why pain arises in muscle spasm is muscle ischemia, (ischaemic muscle pain = a lack of blood flow to your muscle tissues) which leads to a drop in pH and the release of pain-producing substances such as bradykinin, ATP, and H+”
(13)(italics and bold added) ( words added: Ischaemic muscle pain = a lack of blood flow to your body tissues)
Note: A muscle spasm is a term referring to any involuntary muscle contraction, which includes a muscle cramp is defined as an involuntary contraction of a muscle.
..
“Two activating chemical substances are particularly important for the generation of muscle pain: adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and protons (H+ ions) These chemical irritants activate nerve endings by binding to receptor molecules located in the membrane of the nerve ending.”
(14)(italics added)
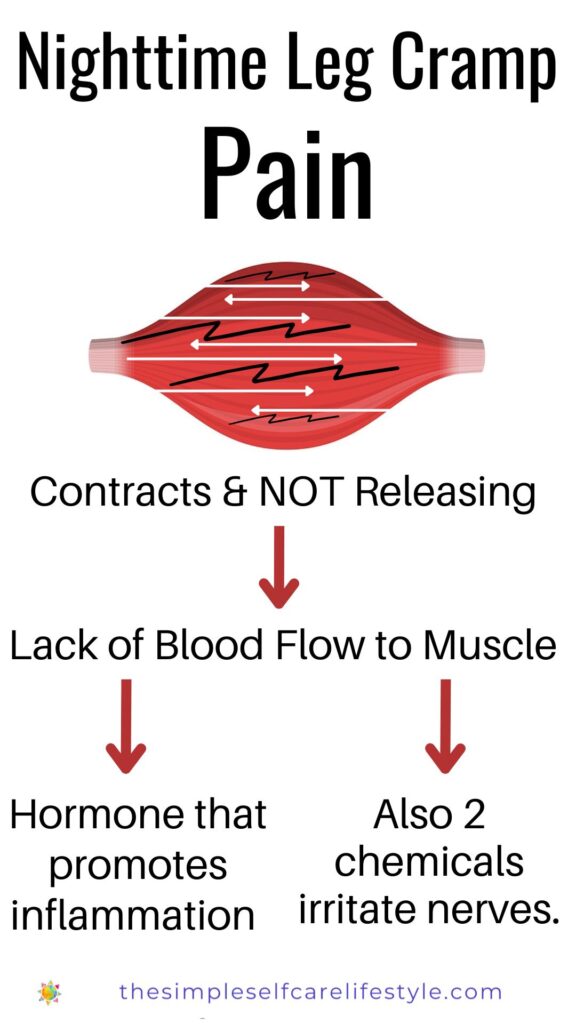
Re-cap:
When your muscle involuntarily contracts and STAYS CONTRACTED, it diminishes the blood flow to the muscle. The lack of blood flow:
- changes the pH, which
- triggers a hormone that produces inflammation, as well as
- two chemical substances that irritate and activate nerve endings.
This is what is causing PAIN in your cramped muscle.
The cascade makes a nighttime cramp painful.
For me and most clients that I used to work with, having a simple understanding of what is happening helps to move through the excruciatingly painful leg cramp without the added layer of fear that can crop up when we don’t know what is causing us to be in pain.
Having a lower sense of fear during the nighttime cramp in itself can lower the escalating pain. Being calmer and clearer also enables us to better- leverage the way the body works, so we can choose and take the best self-care actions.
With a simplified understanding of what makes nighttime leg cramps so painful, let’s explore what we can do to relieve them once they have started.
What Can I Do to Stop the Pain?
To stop the Pain, we need to help the contracted muscle get ‘unstuck’, allowing blood flow to get back into the region.

Stretching the muscle will help do that, and stretching the fibers with Massage can help as well.
Depending on the intensity of the cramp, sometimes getting up and walking can do the trick. For a more intense cramp:
- Standing up and placing pressure on your leg that is experiencing the cramp while slowly elongating it more by placing your hands on the wall and leaning forward. This can help both foot and calf cramps.
- Butt Slide up the wall works well for a Leg cramp that includes your hamstring. (Muscle on the Back of your Thigh)
- If you cannot get out of bed, place a sheet or whatever is near you around your foot and pull it toward you. If you are flexible enough to reach your foot, you can grab it and pull it toward you.
- If someone is right there, you could ask for assistance. For Calf cramps, position yourself face down and bend your knee. Now they can press down on your foot while massaging the calf toward the direction of your knee.
- Using the Rubz massage ball that I shared with you in the Post: Foot Massage Reflexology Benefits Your Entire Body! And Self Care Gifts Post is great for Quads (the front top of your thigh.)
I personally always begin with the wall stretch and move to the downward dog to go deeper.
…The easiest conservative treatment for healthy subjects and patients is stretching the involved muscle or deep massages.
(4)



Re-cap:Stop the pain
To stop the Pain, we need to help the contracted muscle get ‘unstuck’, allowing blood flow to get back into the region. Ways to do that include:
- Standing up and placing pressure on your leg, placing your hands on the wall, and leaning forward.
- Butt Slide up the wall for the back of your thigh.
- If you cannot get out of bed, place something around your foot and pull it toward you.
- If someone is right there, they can press down on your foot while massaging the calf toward the direction of your knee.
- Using the Rubz massage ball for the front of your thigh.
Now let’s move on to why our muscles cramp in the first place and how we can take steps to prevent them from happening.
Why Do Our Muscles Cramp?
Q: Why do we have Nighttime Leg Cramps?
A: There is an Imbalance
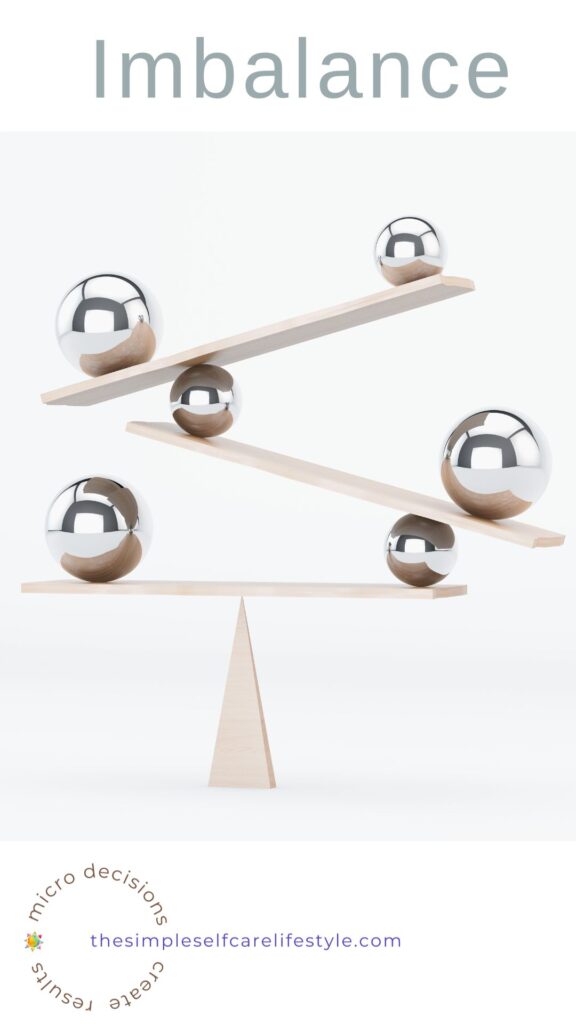

In the research, Nighttime Leg Cramps are noted as having no ‘known one cause’, but rather a multitude of common causes. Each of the Common Causes for Nighttime Leg Cramps points to an imbalance that crosses a threshold and becomes a trigger for the Muscle to involuntarily contract and stay stuck in contraction mode.
The causes of leg cramps are unclear, but some risk factors include pregnancy, exercise, salt and electrolyte imbalances, disorders affecting peripheral nerves or blood vessels, renal dialysis, and some drugs…
(12)
Focus on Your Personal Root Cause
As with every ‘uncomfortable body symptom’ that we experience, our best shot at relieving and preventing the painful symptom of a nighttime muscle cramp is to focus on Optimizing the Body’s Terrain.
Placing the 1 Focus on uncovering your body’s root cramp trigger(s) is what will be most helpful in relieving and preventing them.
Note: There may be more than one cause, and it’s also important to note it may be a different cause that triggers cramps on a different day. Your awareness of common causes will help you head them off.
Let’s move to common causes of leg cramps.
What Causes Nighttime Cramps?

Some Common Causes of Nighttime Leg Cramps
What could be setting your muscle up to contract involuntarily and then remain contracted when you are at rest or sleeping? Some common causes include:
- Underuse of muscles (being too sedentary)
- Overuse of muscles- (excessive exercise or heavy lifting)
- An overstressed nervous system (creating chronic muscle tension).
- Nutrients that are deficient, even subclinically, or out of balance. (Including Hydration)
- Positional compression. (sleeping in a position that is blocking blood flow)
- Certain medications (listed below). Certain Medical conditions.
Pairing Each Common Cause with Simple Self Care
To address each Common Cause, we FOCUS on Simple Self Care that Provides the Skeletal Muscles with what they NEED.
Providing Muscles with Simple Self Care that Provides the Skeletal Muscles with what they need is the way to relieve and ward off leg cramps.
What do Skeletal Muscles Need?
The Skeletal Muscle Tissue needs the cells that they are made of to be healthy. As with all of our body Systems, healthy cells are the foundation, the deciding factor of how healthy and resilient the tissue is that makes up our Systems. (Core Concept 2).
What do Skeletal Muscles Need?
Skeletal Muscles NEED- are dependent on – a daily supply of a few good M.E.N.
YUP! Every day our muscles need a few good M.E.N.: Muscles need balanced Motion, balanced Emotion, and balanced Nutrition.
Incorporating a few good M.E.N. daily is what helps us relieve and then prevent Nighttime Leg Cramps.



What A Muscle Needs Comes Down to:
A few good M.E.N.!
M
Motion. To be Used but NOT Overused, plus Avoid prolonged compression.
E
Emotion: A Balanced Nervous System
N
Nutrition-Macro & Micros Hydrating in a way that DOESN’T deplete Electrolytes
It is our choice of the M.E.N. that we include in our daily lives that provide (or not) what our Skeletal Muscles need for their S.M.I.L.E. (Structure, Machinery, Instruction, Layers, and Energy.)

Placing our energy on the ONE FOCUS: of habitually including a few good M.E.N. in our day results in us having a higher ratio of Healthy Cells. A higher ratio of healthy cells creates RESILIENT, Balanced muscles which do not stay stuck in an involuntary contraction.
Re-cap: Muscles Need
Muscles need balanced Motion, balanced Emotion, and balanced Nutrition. For that they need:
- A daily supply of a few good M.E.N
- Specifically, M.E.N. that will provide what they need for their cells to S.M.I.L.E.
Let’s walk through the Common Causes of Nighttime Leg Cramps and Pair them with Simple Self Care Tips that include the M.E.N. that’ll Provide the Skeletal Muscles with what they need to SMILE.
Common Causes of Nighttime Leg Cramps & Simple Self Care Tips
1
Being Sedentary. Not Using Your Muscles
…a strong association between a sedentary lifestyle and Nocturnal Leg Cramps.…, musculoskeletal conditions associated with sedentary lifestyle17 as well as work postures18–20, prolonged standing21 and western habit of sitting instead of squatting22 have been suspected of causing cramps and specifically NLC. (Nocturnal – Nighttime Leg Cramps)
(17,18,20,21,22)(bold added) (Nocturnal – Nighttime Leg Cramps)
How does not using your muscles trigger nighttime leg cramps?
The body is amazingly frugal with its energy. If you are not using your muscles, it will make use of them.
What does that mean?
The body will register that you are not using your muscles and
- will stop designating resources to them. as well as
- break them down for resources.
Over time, the depletion causes the muscles to be overexcited, overfiring, and move into muscle contractions that can seize up.
The adage is true. Use it or Lose it.
This is why every routine I have ever developed from the 1980s onward uses EVERY MUSCLE.

“Inactivity depletes resources from the muscles, and the muscles respond by being over-excited, leading to muscle contractions.”
(25) (26)(bold added)
“If you stop using your muscles, your body won’t waste the energy it needs to take care of them. Instead, your body will start to break your muscles down, which causes them to decrease in size and strength. “
Common Cause: Underuse of Muscles Depletes then over-excites the muscle reducing blood flow.
Our Lifestyle can promote UNDERUSE of Our Muscles

Simple Self Care Tips for Underuse:
M. MOTION Tip:
1. Move frequently. walk, do stairs, bike, bounce, swim, garden, dance. Don’t complicate it…simply move.
If you are stuck sitting, driving, or standing for long periods and cannot break away for frequent movement, use the Squeeze Release.
I write about Squeeze Release in the post: Improve Lymph System Function. Squeeze Release is helpful in sedentary situations as well. Try it for 60 sec. you’ll be surprised how helpful this simple exercise is.
Aim to use Slide Your Butt Up The Wall exercise for 60 sec. It’ll help elongate your tight, shortening Muscles on the back of your leg, plus help open up your spine at the same time.
Both the release of tight leg muscles and relaxing the spine improve overall posture, which is ultimately beneficial to blood flow and reducing Nighttime Leg Cramps. Really any one-minute movement is enough to make a difference.
Roll your foot up and down. Make circles at the ankle. Have the Rubz ball in your pocket and massage the muscles of your feet. As you roll back and forth, the muscles of the legs will be contracting and help to move blood flow. The key keep moving.
2. Work up to a daily habit of using a SIMPLE Self Care Exercise Routine that incorporates using all your muscles. It can be done efficiently and effectively 15 – 20 minutes tops. (At the start of the day is always best. For no other reason than you will be more consistent.)
If you do not have a quick routine, I have multiple for you On the Videos Topic Page. I have used each of these routines for decades and continue to rotate them.
- 1 Minute Stretches that work on your entire body. I write about the 1 Min Stretching Benefits here.
- Posture Routine that is done in a Chair 2 1/2 min – 20-minute versions Instructions for these videos are included on Neck Hump? Keen Pain? Train this 1 Muscle First Post.
- 90 Days 5 Simple Exercises The Routine builds over 90 days, and the maximum time is 15 minutes. You can have it dripped weekly to your inbox.
M.& E. MOTION & EMOTION Tip:
Place Your Legs Up the Wall. At the end of each day, or after a long sitting or standing situation, I am always sure to Place my Legs Up the Wall for a few moments. This helps multiple body systems. Two big ones are:
- The Vascular system (carries our blood flow back up toward our heart) Using Legs Up The Wall helps to redistribute the blood flow up and out of my lower legs.
- Legs Up the Wall also helps calm the Nervous System. I place my legs up the wall each night without fail because it definitely calms my Nervous System for better sleep. I layer on 4 Rounds of the 4-7-8- Breathing for my HPA Axis. Legs Up the Wall with HPA Axis Breathing definitely reduces nighttime leg cramps for me.
Simplified Re-cap for Underuse
- Move Frequently
- Form a Habit of Doing a Simple Daily Routine that Uses All Muscles.
- Use Squeeze Release throughout the day if you are unable to move much.
- Use Legs Up Wall with the 4-7-8 breathing to Support the Legs and Nervous System.
There are a lot of Simple Self Care options when it comes to helping our Underused Muscles SMILE.
Pick what fits into your life the best. Use the MOtivator App to build MOtivation. It rewards your brain for making the Micro Decision to take on one of these SIMPLE Self Care Actions.
Let’s move to the next Common Cause of Nighttime Leg Cramps: Overusing Muscles.
2
OVERUSING Muscles
…“Muscle voluntary contractions …decreases the net blood flow to the working muscle and induces fatigue” “When doing particularly intense physical activity, the nerves in your spine can become overexcited and fire involuntarily, contracting your muscles and causing a cramp.” “Muscle overload and fatigue results in a localized muscle cramp”.
(27) (bold added) (24)(28)
Overuse of Muscles Reduces Blood Flow

Extreme or unaccustomed eccentric exercise can cause exercise-induced muscle damage, characterized by structural changes…altered calcium homeostasis, disruption of excitation-contraction coupling, as well as metabolic changes bring about loss of strength. Importantly, the trauma also invokes an inflammatory response”
(28)(bold added)
EXERTION
There are benefits to training hard and exerting yourself; then there is OVER exertion. It is important to exert yourself, layering on challenges to your muscles slowly. Done this way, they have time to strengthen. This will enable you to exert yourself more and more over time safely.
OVEREXERTION
Overexertion, on the other hand, is going over your muscle’s abilities, causing disruption of the nervous system signals, inflammation in the muscles, and often dehydration and mineral imbalances/depletion. (28)
Simple Self Care Tips for OVERUSE
M. MOTION Tip:
Prevention tips:
- Get in the habit of using the E for E technique that helps stabilize your core muscles. A stable core reduces calling on your leg and back muscles in ‘excess’. I cover this invaluable breathing in the Post titled Incontinence, ED, Pelvic Floor, Back Issues. Use the breathing technique E for E breathing with Everyday activities and also while exercising and/or Heavy Lifting. E for E protects you and helps reduce unexpected overuse of muscles.
- The Chair Routine is amazing at strengthening your core muscles by training your diaphragm first. Having a strong diaphragm improves your overall muscle strength capabilities. I share how to train your diaphragm- Your Spines #1 stabilizer in Neck Hump? Train this Muscle First. Training your diaphragm is a fantastic way to prevent/reduce the negative impact of heavy lifting and increase your muscle exertion capabilities safely.
Recovery Tips for Overused Muscles
- REST!
- Legs Up the Wall supports the leg’s vascular, spine, and nervous systems. Exponential benefits for small time investment.
- Ice packs on the region of inflammation from excess exertion.
- Infrared sauna or L.E.D. device. I sauna each day, and when in need of extra support, I have used my L.E.D. device with great success. I open the neck and decollete L.E.D., and place it directly on my muscle.
L.E.D. is Light-Emitting Diode. “Light-emitting diode therapy can be useful to reduce muscle damage, pain, and atrophy, as well as to increase muscle mass, recovery, and athletic performance in rehabilitation programs and sports medicine“ (29)
5. Using Arnica Gel or Cream and pellets immediately and also increasing my Serrapepdase. helps. Everything mentioned can be found on the Things I Keep Handy for Life’s Little Emergencies and Personal Products Pages.
6. Magnesium Sulfate (Epsom Salts) is helpful to many for muscle recovery. Soak in it. If there is no tub, do a foot soak. You can also use spray. I make my own spray bottle with water and Epsom salts to keep handy.
“Magnesium plays an important role in muscle recovery. It helps to reduce inflammation, and therefore reduces the amount of muscle soreness and fatigue that can occur after a workout”
“regulate nerve impulses, which can help reduce cramping, as well as increasing oxygen delivery to the muscles”
(30) (Bold and italics added)
E. EMOTION Tip:
- Here again, Legs Up The Wall with 4-7-8 Breathing is a beneficial combo for your Nervous System which supports the relief/prevention of cramps Leg Cramps.
N. NUTRITION Tip:
- Hydrate: Hydration is vital to preventing muscle cramps. You want to be sure you hydrate in a way that replaces or maintains your Mineral Balance. (I detail how to do this below in the Common Cause: Nutrition section, which is next)
Why is Hydration a tip when it comes to muscle exertion?
The reason hydration is also listed under muscle exertion is because dehydration can cause muscle tension.
Dehydration-induced muscle tension increases your risk of exceeding the muscle’s capabilities (overexertion).
Dehydration-induced muscle tension is why on warmer days or days you sweat more; you can exceed your muscle’s ability quicker than you normally would.
A cramp may come as a surprise since you are doing what you do normally. The dehydration-induced muscle tension is the cause of you overexerting quicker, causing muscle cramps.
Knowing this tip can help you avoid dehydration-induced muscle tension that pushes into overexertion of your muscle.
2. Magnesium Bath. EPSOM SALT Bath, Foot Bath, or Spray.
3. MACRO Nutrients. Macro Nutrients are your Fats, Proteins, and Carbs. All are needed. Protein is particularly important in the recovery from overexertion. (31) We do not store Protein, so I am always sure to have a portion for each of my main meals and even snacks. We need more complete protein to recover from overexertion AND also as we age. I have 3 Protein Posts for you:
Simplified Re-cap: Overuse
Preventative:
- Use E for E Technique along with daily postural exercise.
To Recover from Overexertion:
- Rest!
- Legs Up Wall with 4-7-8 Breathing
- Arnica/Serrapeptase
- Ice/Epsom Salt (Magnesium Sulfate) Bath/Spray
- Infrared Sauna/L.E.D. Light Therapy
- Hydration
- Protein
3
An overstressed nervous system = chronic muscle tension.
Muscle Tension; Anxiety causes a considerable amount of muscle tension, and muscle tension can lead to both cramping and spasms. Muscle tension is a lot like exercise – it tires out the muscles and causes them to spasm as a result.
(25)
Chronic Muscle Tension Can Reduce Muscle Blood Flow

A cramp in your legs at night does not automatically mean you underused or overused your muscles or that there is dehydration-induced muscle tension.
Nighttime Leg Cramps Can Be The Result of Other Muscles in Your Body Being Tense.
Muscle tension, especially chronic muscle tension in other parts of your body, for example, the neck and shoulders or back, can result in Nighttime Leg Cramps due to the stress hormonal cascade. (10)(32)
It is important to note that a painful contraction that is limited to a specific area does not mean that the cause of the cramp is necessarily local.
(4)
A cramp is almost never a local effect but involves the whole body system, such as somatic and emotional.
This is in line with Core Concept 1 of our 1 FOCUS. Our Body is made up of systems that are ALL interconnected and interdependent on each other. There is an ongoing crosstalk between all parts of our body. All our Motions. All our Emotions, and all our Nutrition impact every single System.
Simple Self Care Tip
M. MOTION Tip:
1. Move frequently to loosen up tension-filled muscles. Walk, do stairs, bike, bounce, swim, garden, dance. Don’t complicate it…simply move.
If you are stuck sitting, driving, or standing for long periods and cannot break away for frequent movement, use the Squeeze Release.
2. Squeeze Release in the post: Improve Lymph System Function. Squeeze Release to move blood flow into the tension-filled muscles. Try it for 60 sec. you’ll be surprised how helpful this simple exercise is.
4. Do the Chair for 2 1/2 minutes, Breathing, Epsom salt bath to unwind. —
5. Only have a Minute that works too!
E. EMOTION Tip:
- Here again, Legs Up The Wall with 4-7-8 Breathing is a beneficial combo for your Nervous System which supports the relief/prevention of cramps Leg Cramps.
N. NUTRITION Tip:
- Hydrate: Hydration is vital to preventing muscle cramps. You want to be sure you hydrate in a way that replaces or maintains your Mineral Balance. (I detail how to do this below in the Common Cause: Nutrition section, which is next)
- Eat fruits and veggies that work FOR YOUR BODY that have a higher water content.
- Wean off the Caffeine:
Regular consumers of caffeine had higher muscle tension after three or more hours of abstinence than low caffeine consumers. (33)
…anxiety was highly correlated with prior caffeine use, suggesting that even a brief abstinence may produce anxiety in the regular user (33)
Caffeine is a diuretic, meaning it will cause your body to let go of fluid a cause for dehydration…”urinary output and natriuresis were significantly increased by caffeine” (34)
Caffeine increases muscle tension, anxiety that provokes muscle tension, dehydration-induced muscle tension.
(33)(34)
Remember, caffeine is a drug, and its impact on your body needs to be compensated for. I’ll be focusing on caffeine in a future post for now, it’s good to know:
- Caffeine-induced muscle tension rears its head around 3-4 hours post-drink.
- Anxiety-induced muscle tension is a common result of caffeine intake.
- Dehydration-induced muscle tension can originate from caffeine promotion of urinary output.
All muscle tension, regardless of what created it, sets your muscles up to cramp more easily.
Re-cap: stress-Tension-Anxiety
- Chronic Muscle Tension Reduces Muscle Blood Flow.
- Reduced Blood flow in one area of the body impacts all the areas of the body.
To Reduce Muscle Tension:
- Move frequently
- Legs Up Wall with 4-7-8
- Hydrate
- Eat fruits and veggies with higher water content (those that work for your body)
- Wean off caffeine
I bet you noticed a lot of the M.E.N. are repeating.
you are right!
There are Foundational Simple Self Care Actions we can incorporate into our lives that support and improve a multitude of Body Symptoms and conditions.
Self Care does NOT need to be complicated. Often the biggest hurdle is helping people believe that consistently doing the ‘SIMPLE Self Care’ routines while swapping out Toxins is enough to make a difference. It does! It is! Consistently making Simple Self Care Micro-Decisions are what will support your body in a way that gets you long-lasting results!
It is the beauty of the 1 Focus, 1 Goal, and 1 Micro Decision at a time Self Care Lifestyle.
You get to skip the overwhelm, stay focused on doable self-care actions, and reap exponential results!
THe simple self care lifestyle
Simplify
Let’s keep going. We have three more Common Causes for Muscle Cramps.
4
Nutrients that are deficient, even subclinically, or out of balance.
Although water and the principal electrolytes (sodium, potassium, and chloride) are often excluded from lists of nutrients, these substances are essential dietary components.
(35)
Dehydration/Mineral Imbalance and High Diuretic-Low Water Content Foods Common Causes of Leg Cramps

- Hydration – We’ve covered the importance of staying hydrated. I just want to expand on the importance of hydrating in a way that we do not reduce our minerals because reduced minerals are a Common Cause of Nighttime Cramping.
- Replenish Vitamins and Minerals. It is important that we pay special attention to vitamins and minerals in hot weather. As we sweat, the body depletes both water-soluble vitamins and minerals.
Replenish minerals, especially electrolytes.
Nutrition is a behemoth topic. Staying super focused on the most common cause of muscle cramps it is important to include Hydration, Vitamins, Minerals, especially Electrolyte Minerals.
The body cannot produce micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) on its own and, therefore, micronutrients must be supplied through dietary intake.
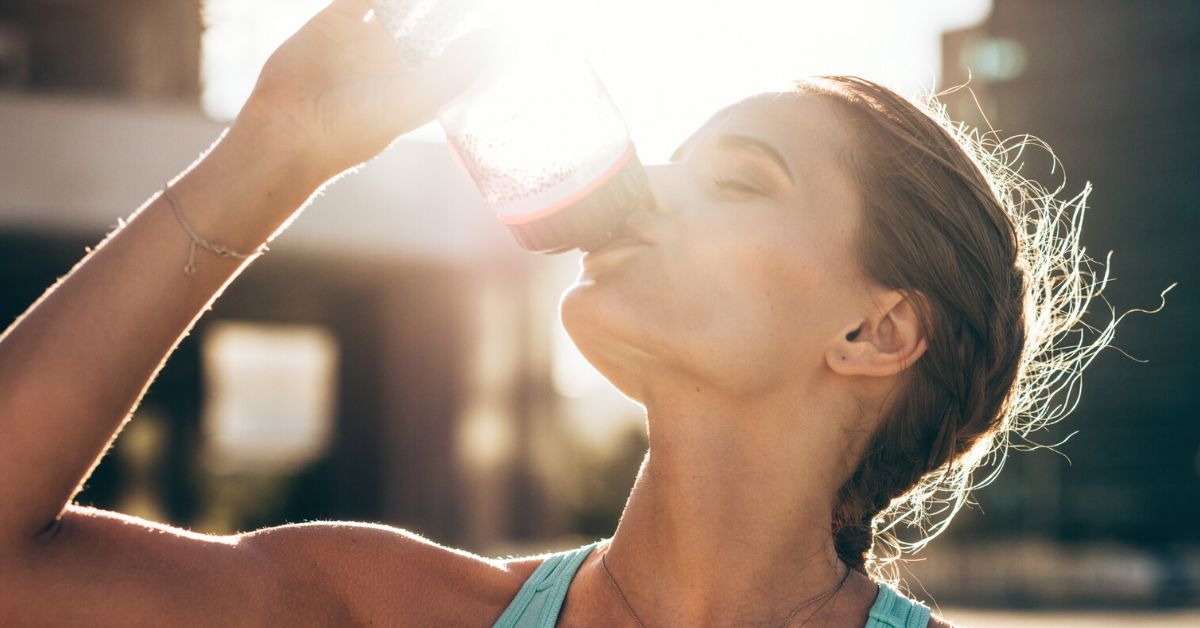

Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride and calcium) need to be in balance in order to maintain healthy blood, heart rhythm, muscle function and other important functions. Drinking too much water, can cause the electrolyte levels in the body to get out of whack and cause sodium levels plummet.
It is important to know that “Drinking too much water can cause the electrolyte levels in the body to get out of whack and cause sodium levels to plummet” The mineral imbalances can promote leg cramps..
Simple Self Care Tips
So while it is GREAT to increase your hydration, when it comes to avoiding cramps, you want to keep in mind that with extra hydration, it is important to stay on top of your water-soluble vitamins and minerals. The best way and simplest way I have found to keep hydration up without depleting important minerals when I am sweating more is to:
- drink mineral water
- drink water with 8 drops of cell food
- increase the balanced mineral supplement that I use
- daily Mag phos and 12 Schuessler Salt Combo
- increase high-water foods
- zero caffeine
I’m always good at drinking, so the majority of the heat-induced cramps I experienced stemmed from water-soluble vitamin and mineral loss. I cannot tell you how life-changing it was for me and many clients with the consistent incorporation of the above list, especially each Summer.
Re-cap: Deficiencies or out of balance. (Including Hydration)
- Hydrate if you can with Mineral Water or
- A cold herbal tea like Hibiscus that is High in Vitamin C, add a splash of fruit…
- Skip the low water content Foods and caffeine and instead enjoy high water content foods that work for your body.
- For extra support, Balanced Minerals/Cell Salts
NOTE: the Hibiscus tea I use is on the Quality Foods page. The reason I use this brand is in the Post: Plastics in your Tea Bag? Yup! Billions in each cup.
I’ve also listed the cell drops, mineral supplement, and cell salts that I use on the supplements page. It might be a good place to start with your practitioner.
Next up:
5
Positional Compression while Sleeping.
…lying in a certain way that restricts movement or blood flow to the legs, such as resting one leg on the other or crossed, may lead to cramps.” ” it is also said that ” Sleeping with the foot stretched out and the calf muscles shortened may trigger night cramps.”
Sleeping Positions and/or Heavy, Tight Bedding are Common Causes of Nighttime Leg Cramps

Changing sleeping positions isn’t exactly easy. But a couple of hacks have worked for my clients over the years.
Back sleepers are all set when it comes to positioning. There is no compression to speak of. Back sleepers are the ones though, that want to be doubly sure the bedding is not too tight or heavy.
Simple Self care Tips:
- Stomach Sleepers Have your feet hang off the end of the bed.
- Side Sleepers get a firm body pillow so you can support your leg without pressing on your bottom leg.
- Sleep with blankets that are not too heavy and that are not tucked in tight. The easier it is for you to move around under them, the better.
The Favorite Sleeping Hack for Stomach Sleepers.
Hands-down clients who are belly sleepers raved at the difference it made not only for leg cramps but for their backs when they positioned their feet off the end of the bed. I never really thought of it as a hack because that’s always been the way I sleep.

The Favorite Hack for Side Sleepers.
Sleeping with a firm body pillow. This allows the top leg to be supported and reduces the chance of the bottom leg having its blood flow restricted.
Re-cap: Compression while sleeping
- Stomach Sleepers: Have your feet hang off the end of the bed.
- Side Sleepers: Get a firm body pillow so you can support your leg without pressing on your bottom leg.
- All Positions: Sleep with blankets that are not too heavy and that are not tucked in tight. The easier it is for you to move around under them, the better.
Last but not least: Medications and Medical Conditions.
6
Certain Medications/Medical Conditions can cause leg cramps.
Predisposing factors could include electrolyte disturbances or neurological disorders, hormonal and metabolic disorders, and compressions of nerve roots or compressed arterial vessels. Other predisposing factors could be related to the constant consumption of drugs, such as diuretics, beta-blockers, and statins.
(4)(bold added)
Some Medications and Medical Conditions can contribute to Nighttime Leg Cramps

If you have been sleuthing for your root cause but have not been successful with figuring it out and you happen to be on medications or have a circulatory or any condition, really team up with your practitioner, share with them what you have done, and see if your medication or condition might be playing a role and what suggestions they may have.
Sometimes understanding the medication side effects and what nutritional deficiencies they may create over time can be counteracted by proper supplementation.
Kidney issues, diabetic nerve damage, problems with blood flow, neurological disorders, hormonal and metabolic disorders, and compressions of nerve roots or compressed arterial vessels are known to cause night leg cramps.
Simple Self Care Tip
- Read the pamphlet that comes with your medication.
- Talk to your practitioner.
- Have your vitamin/mineral levels checked. Sometimes the medicines can create a deficiency that can be restored and maintained. ALWAYS check with your practitioner before adding supplements when you are on medication. ALWAYS.
Listed Medicines that are possible contributors to Leg Cramps:
A List from Multiple Sources of Medicines that have leg cramps as a side effect include:
Cleveland Clinic(1)
- Albuterol/Ipratropium (Combivent®).
- Conjugated estrogens.
- Clonazepam (Klonopin®).
- Diuretics.
- Gabapentin (Neurontin®).
- Naproxen (Naprosyn®).
- Pregabalin (Lyrica®)
- Statins.
- Zolpidem (Ambien®).
- Sertraline (Zoloft®).
- Fluoxetine (Prozac®).
- Celecoxib (Celebrex®).
Medical News Today(2)
- intravenous iron sucrose (Venofer)
- naproxen (Aleve)
- teriparatide (Forteo)
- raloxifene (Evista)
- levalbuterol (Xopenex)
- albuterol/ipratropium (Combivent)
- conjugated estrogens (Duavee)
Others:
- Conjugated estrogens (Premarin)
- Iron sucrose (Venofer)
- Potassium-sparing diuretics: Examples include triamterene (Dyrenium), spironolactone (Aldactone) and eplerenone (Inspra).
If you are taking medication, it is always best to read your medication’s complete list of side effects and converse with your practitioner.
Re-cap: Medication/Medical Conditions
- Some Medications can contribute to Nighttime Leg Cramps.
- Also, some Medical Conditions can contribute to Nighttime Leg Cramps. Kidney issues, diabetic nerve damage, problems with blood flow, neurological disorders, hormonal and metabolic disorders, and compressions of nerve roots or compressed arterial vessels are known to cause night leg cramps.
- Team up with your practitioner to explore possible supportive steps.
Bottomline: The Key to Relieving Nighttime Leg Cramps
The key to effectively relieving and preventing nocturnal leg cramps is uncovering where the imbalance is rooted.
Awareness of your personal imbalances that are contributing to your nighttime leg cramps makes it easier for you to choose the Simple Self Care Tips that’ll work for you.
PLUS, you can’t go wrong since each Simple Self Care Tip simultaneously supports the 1 GOAL of Optimizing Your Terrain. WIN-WIN.
Once you can identify the possible imbalance(s) (always our number 1 Self Care Goal), you can add
A few good M.E.N.!
- So your Muscles will be Used but NOT Overused.
- Your Nervous System will be more balanced.
- Nutrients: Macro and Micro, Including Hydration, will be supportive.
We dove into each of the M.E.N. and how they fulfill the Skeletal Muscle needs, along with the Simple Self Care Tips that Leverage the way the body is set up to work for the best results. You’ve got this! I’d love to hear what improves your nighttime cramps. You can email me: simplifyselfcare@gmailcom



Remember your efforts are always a WIN-WIN because, as you are Providing your body with what’s missing and Eliminating stressors, you will be optimizing your body’s terrain.
THe simple self care lifestyle
Simplify
The Simple Self Care Lifestyle
References for you
1 Leg Cramps. Cleveland Clinic. Professional, C. C. medical. (n.d.).
8 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2023, March 7). Muscle Cramp. Mayo
9 Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/muscle-cramp/symptoms-causes/
References for you continued
12 Young G. Leg cramps. BMJ Clin Evid. 2015 May 13;2015:1113. PMID: 25970567; PMCID: PMC4429847. .
References for you continued
References for you
References for you
30. Hall, T. (2023, April 16). Magnesium: The mineral you need for muscle recovery. ASFA.
References for you
34. Ganio MS, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. Evidence-based approach to lingering hydration questions. Clin Sports Med. 2007 Jan;26(1):1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.csm.2006.11.001. PMID: 17241912.